The USA is facing a debt crisis and needs an urgent upgrade of its debt ceiling by the US Congress. The current US debt amounts to $ 31.3 trillion, which is increasing every second. The maximum US debt ceiling set in December 2021 to $31.4 trillion dollars. Recently, the US treasury secretary declared that the USA will not be able to meet its financial obligation after 1st June 2023 if the debt ceiling is not raised.
What is the US Debt?
The US debt refers to the accumulation of a substantial national debt owed by the US government. The primary cause of the US debt is the persistent gap between government spending and revenue, resulting in budget deficits. Factors like increased government spending, tax cuts, pandemic, and economic depressions contribute to the rising debt of the USA.
The US debt is resolved by issuance of government bonds and borrowing from domestic and foreign entities.
The total debt of the USA is measured publicly-held debt, i.e. debt owed to external investors, and intragovernmental debt, i.e. debt owed to other government agencies.
Currently, 24% of the total US debt is owned by China, Japan, the UK, and other oil-exporting nations. Moreover, a third of the total US debt is owned by domestic investors. Thus, any failure by the USA to repay its debts may result in a global crisis.
Causes of USA’s rising debt

One of the primary reasons for the debt crisis is the significant increase in government spending over the years. This includes spending on various programs, defense, entitlements, infrastructure, and more. Additionally, persistent budget deficits for many years have contributed to the rising of the total US debt.
Moreover, tax cuts and certain taxation policies have reduced government revenue; thereby leading to a widening gap between income and expenditure. The current economic recession in the USA, failure of several banking institutes, increased government spending on welfare programs, and increased expenditure on warfare are a few major contributors to the rising US debt.
A consequence of rising US debt is the increased interest on the total accumulated US debt. As the debt grows, the interest payments increase; thereby, consuming a larger portion of the budget. Therefore, the situation continues in a vicious cycle of debt. This debt cycle can only be broken by instituting strict fiscal reforms.
US debt ceiling and its related economic impact

The US debt refers to the policy of the nation to spend more than it generates. The current debt implies that the USA spent 1.5 times more than it earned through taxes and revenues. The US government expenditure in payroll and programs far exceeds its total revenue generation. The US debt is a growing economic crisis. Increased US debt leads to increased loan interest, inflation, and reduced funds for government programs. The US government fiscal policies strongly influence the total US debt. The rising healthcare costs also contribute to the increasing national debt leading to a debt crisis.
The US President and the Congress set a ceiling to the amount of debt the country can accrue. The US government has needed to increase its debt ceiling almost every Presidential term. Whenever the US debt ceiling is raised, it allows the US government to borrow more money to fund its operations. The government primarily borrows more money by issuing treasury bonds, notes, and bills.
Who owns the US debt?
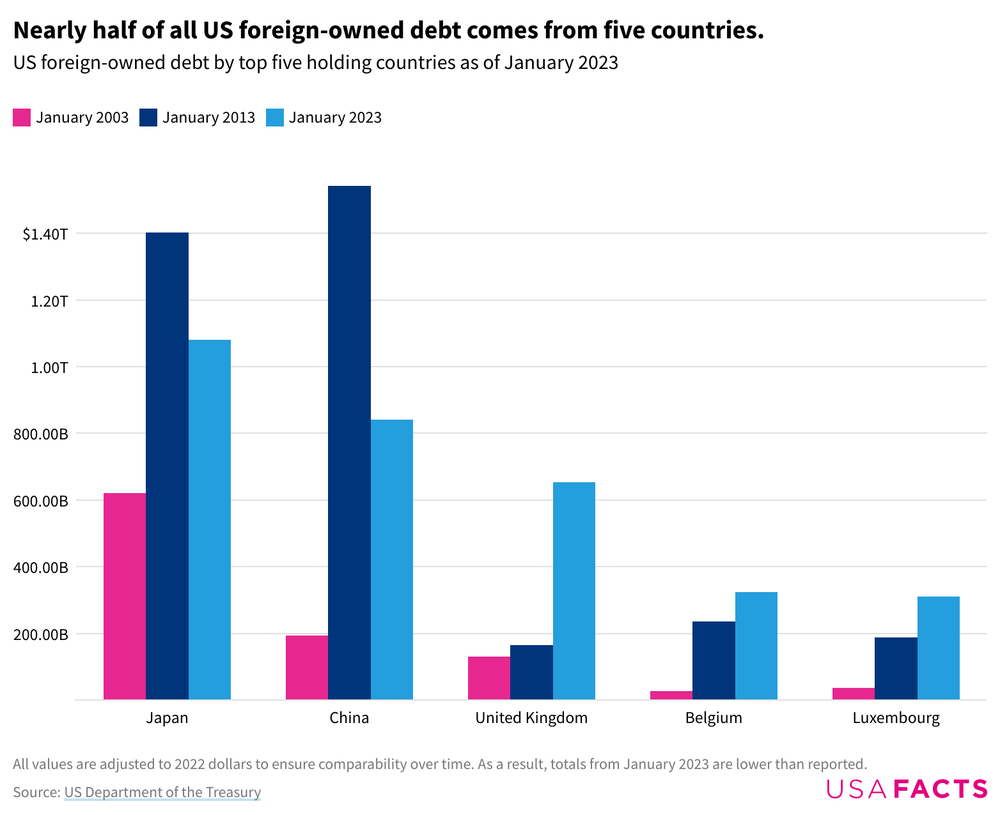
The financial instruments or securities issued by the US government are purchased by domestic and foreign entities. The domestic purchasers of these securities are private individuals, institutional investors, banks, pension funds, foreign governments, and central banks.
The largest holder of US debt is the federal government itself. The government invests in itself by buying the debt securities using pension funds, mutual funds, and healthcare funds. However, raising the debt ceiling does not provide the US government with additional money to spend. It simply allows the government to borrow the necessary funds to fulfill its obligations. The US government is responsible for paying back the debt with interest to the investors who hold these securities over time.
As the US debt crisis intensifies, it increases global concerns about the sustainability of the US government debt. Investors may demand higher interest rates on the US Treasury bonds; thereby, leading to increased borrowing costs for the US government on the whole. Therefore, the US debt crisis potentially impacts global interest rates and inflation dynamics.
The US debt and De-dollarization

The US dollar currently holds the position of the world’s dominant reserve currency. The current US debt crisis undermines global confidence in the US dollar’s stability; consequently, it may prompt countries to seek other alternatives. This could potentially accelerate the process of de-dollarization, where countries reduce their dependence on the US dollar in international transactions.
The US debt crisis may lead some countries to reevaluate their economic ties with the United States. They could seek to strengthen regional trade agreements, promote local currencies for trade settlement, or explore alternative reserve currencies such as the euro, yuan, or digital currencies. This could gradually reduce the US dollar’s influence in global trade and finance.
The status of the US dollar as the global reserve currency has significant geopolitical implications. Any major shifts in de-dollarization could alter the geopolitical balance of power, affecting the influence and reach of the United States in global affairs.
Conclusion
The impact of the US debt and the US debt crisis on de-dollarization and global economy is very complex. There are several various factors that influence the global response to the current US debt crisis. The US government needs to rethink its taxation schemes and government programs to enable a stable economic growth in the country. A comprehensive approach involving fiscal discipline, budget reforms, economic growth, and long-term planning may allay the fears of debt crisis for the nation.
References