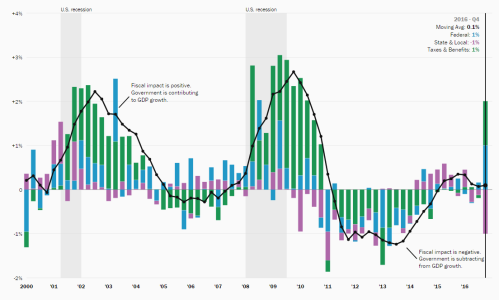
The Hutchins Center Fiscal Impact Measure shows how much local, state, and federal tax and spending policy adds to or subtracts from overall economic growth, and provides a near-term forecast of fiscal policies’ effects on economic activity.
https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/interactive-12-2023.csv
FEDERAL, STATE AND LOCAL FISCAL POLICY AND THE ECONOMY
By Eli Asdourian, Georgia Nabors, Lorae Stojanovic, and Louise Sheiner
Fiscal policy increased U.S. GDP growth by 0.4 percentage point in the third quarter of 2023, the Hutchins Center Fiscal Impact Measure (FIM) shows. The FIM translates changes in taxes and spending at federal, state, and local levels into changes in aggregate demand, illustrating the effect of fiscal policy on real GDP growth. GDP increased at an annual rate of 4.9% in the third quarter of 2023, according to the government’s latest estimate.
A decline in tax collections in 2023 increased the FIM by 0.8 percentage point in the third quarter, while strong increases in state and local purchases boosted it by an additional 0.7 percentage point. These effects were partially offset by the waning effects of pandemic-era transfers and subsidies, which decreased the FIM by 1.1 percentage points.
Fiscal policy provided significant support to economic growth when large swaths of the economy were shut down in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. The FIM turned negative in the second quarter of 2021 as fiscal support waned. Since the beginning of 2023, the FIM has been close to neutral. Barring any changes in tax or spending legislation, we expect the FIM to remain roughly neutral through the end of 2025.
The FIM tracks the influence of fiscal policy on GDP growth rates. It measures only the direct impacts of fiscal policy on demand (including both discretionary fiscal policy and automatic stabilizers). It doesn’t include fiscal multipliers nor any potential effects of fiscal policy on aggregate supply. For an analysis that includes multipliers, as well as a more detailed breakdown of the components of the FIM, read our explainer on how pandemic-era fiscal policy affects the level of GDP, which includes a comparison of actual GDP with our estimate of what GDP might have been had fiscal policy failed to respond to the pandemic.»
For more on the FIM, see our methodology ». You can also read our Guide to the FIM ».