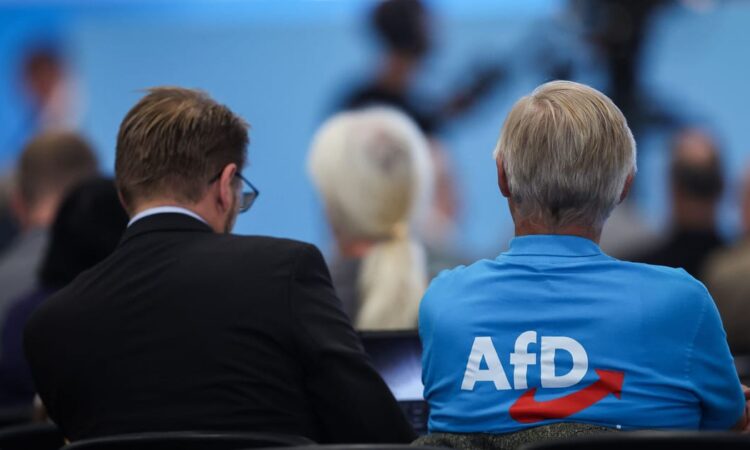
Mathias Döpfner is chairman and CEO of Axel Springer, POLITICO’s parent company.
In Germany today, the right-wing populist Alternative for Germany (AfD) is maintaining a stable 20 percent in opinion polls — coming in two to four points ahead of the ruling center-left Social Democratic Party (SPD) and running hard on the heels of the center-right Christian Democratic Union (CDU).
In some federal states, the AfD is already the strongest party. In Thuringia, for example, it has reached 34 percent, meaning the party has three times as many supporters there as the SPD. And in some administrative districts, around half of those eligible to vote are leaning toward the AfD. According to one Forsa survey in June, the AfD is currently the strongest party in the east of Germany — a worrying trend with elections due this year in Bavaria and Hesse, and next year in Thuringia, Saxony and Brandenburg. And, of course, there are also the European Union elections in 2024.
However, this rapid rise should come as no surprise. The writing has been on the wall for a long time. And more than anything else, the party’s recent advances are a result of an increasing sense among broad swathes of the population that they aren’t being represented by traditional political and media elites.
This disconnect was first accelerated by the refugee crisis of 2015, then increased during the pandemic, and has since escalated in response to the increasing high-handedness of the “woke movement” and climate politics. Just a few weeks ago, a survey by the German Civil Service Association revealed trust in the government’s ability to do its job is at an all-time low, with 69 percent saying it is deeply out of its depth.
Meanwhile, opinion polls show the government fares particularly badly in Germany’s east. A rising number of people — including the otherwise stable but also staid middle classes — now feel enough is enough, and no other party is as good at exploiting this feeling as the AfD.
The problem, however, is the AfD isn’t a normal democratic party.
The regional offices of Germany’s domestic intelligence services in the federal states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Saxony, Lower Saxony and Baden-Württemberg have all classified their local AfD associations as “organizations of interest.”
And the same applies at the federal level. The national office of the domestic intelligence service, the remit of which includes protecting the German constitution, has also classified the national party of the AfD as “of interest.”
These concerns about the party’s commitment to the constitution aren’t unjustified. In a 2018 speech at the national conference of the party’s youth section, Junge Alternative, former AfD chairman Alexander Gauland said that “Hitler and the Nazis are just a speck of bird shit in a thousand years of successful German history.”
When speaking about the Holocaust Memorial in Berlin, Björn Höcke, group chairman of the AfD in Thuringia, said on 2017 that “We Germans — and I’m not talking about you patriots who have gathered here today. We Germans, our people, are the only people in the world to place a monument of shame in the heart of our capital city.”
And in a speech in the Bundestag in 2018, party boss Alice Weidel bandied about terms like “headscarf girls” and “knife-wielding men,” while her co-chairman Tino Chrupalla speaks of an “Umvolkung” — that is, an “ethnicity inversion” — which comes straight out of Nazi ideology.
This small sample of public statements leaves no doubt that such utterings aren’t slips of the tongue — they reflect these leaders’ core beliefs.
And while many vote for the AfD out of protest, more than anything else, the party feeds off resentment and fear, exploiting and fueling anger, hate and envy, pushing conspiracy theories to hit out at “those at the top,” as well as foreigners, Jews, the LGTBQ+ community or just about anyone who might be deemed different. And the party leaders’ blatant admiration for Russian President Vladimir Putin exposes their reverence for autocracy.
Failure to prevent the AfD’s rise could potentially first corrode, then shatter democracy and rule of law in Germany.
But how can a party like this, which is getting stronger in the polls, be dealt with? Is a ban the right way to go? They are always difficult to deal with, and it isn’t even an option at this stage. What about joining the AfD to form a coalition and temper the party? That is even more difficult, as it is unreasonable to argue that the AfD should be treated like other parties. The Nazis and Adolf Hitler had also been democratically elected when they seized power in 1933.
So, what options remain? Many politicians and journalists say we need to confront the AfD with critical arguments. Sounds good on the face of it. But people have already been doing that for a decade — with scant success.
This is why the only remaining option is to attempt what neither the AfD nor many politicians from established parties have been able to do: Start taking voters’ most important concerns and issues seriously, and seek to find solutions.
The fears that have allowed the AfD to become as big as it is today are clearly identifiable. When a recent survey by Infratest Dimap asked “What topics most influence your decision to vote for the AfD at the moment?” 65 percent said immigration, 47 percent said energy policies and 43 percent named the economy.
And in their handling of all three of these key issues, the older parties have demonstrated moral cowardice and a lack of honesty.
This is especially apparent when it comes to immigration.
Why is it so hard for centrist politicians to just come out and say a few simple truths? Germany is a land of immigration, and it must remain so if it wants to be economically successful. And modern migration policy needs a healthy balance between altruism and self-interest.
According to economists’ most recent estimations, Germany needs to bring in 1 to 1.5 million skilled individuals per year from abroad. What we need is an immigration of excellence and qualified workers. People from war zones and crisis regions should obviously be taken in. But beyond that, we can only take the migrants we need, the ones who will benefit us.
This means the social welfare benefits for immigrants require critical rethinking, with the goal of creating a situation where every immigrant would be able to and would have to actually start working immediately. Then add to this factors that are a matter of course in countries with a successful history of integration: learning the local language and respecting the constitution and the laws. And anyone who doesn’t must leave — and fast.
Germany’s current immigration policy is dysfunctional. Most politicians and journalists are fully aware of this, but they just won’t say it out loud. And all this does is strengthen the AfD, as well as other groups on the left and right that have no true respect for democracy.
Not speaking out about the problem is the biggest problem. Indeed, when issues are taboo, it doesn’t make the issues any smaller, just the demagogues stronger.
We’re seeing the same with energy policy. Everyone knows that in the short term, our energy needs can’t be met by wind and solar power alone. Anyone interested in reality knows decarbonization without nuclear power isn’t going to be feasible any time soon. And they know heat pumps and cutting vacation flights won’t solve the global carbon challenge — it will, however, weaken the German economy.
We need only look at one example: While just over 2 percent of global carbon emissions come from aviation, almost a third are caused by China — an increasing amount of which comes from coal-fired power stations. Ordinary Germans are very much aware the sacrifices they’re being asked to make, and the costs being piled on them, make no sense in the broader scheme of things, and they’re understandably upset.
In some cases, this makes them more likely to vote for the AfD.
This brings us to the third and final reason why people are so agitated. The EU, and above all Germany, has broken its promise about advancing prosperity and growth. Fewer young people now see a future for themselves in Germany; more and more service providers and companies are leaving; and the increasing number of immigrants without means is reducing the average GNP per capita. Germans aren’t becoming more prosperous — they’re becoming poorer.
Traditional politicians and political parties unable to offer change are thus on very shaky ground. They have disconnected themselves from their voters, and they are paving the way for populists who use bogeyman tactics and offer simplistic solutions that solve nothing.