
Published as part of the The international role of the euro, June 2023.
Movements in the exchange rates of major reserve currencies as well as in the market prices of securities held by central banks may have a significant impact on the currency composition of official foreign exchange reserves, when measured at current exchange rates. For instance, a broad US dollar appreciation, as was the case in 2022, mechanically increases the share of the US dollar, as other currencies lose value against that currency. Similarly, if yields increase, the market value of bonds falls, leading to a stronger decline in the value of reserve assets denominated in currencies experiencing the largest decreases in bond prices. These developments, as noted by Chinn et al. (2022)[1], confound active reserve management strategies through changes in the value of the underlying assets. This box reviews the evidence of the importance of these valuation effects for the adjustment of currency portfolios by reserve managers against the background of large fluctuations in exchange rates and bond prices seen in the past year.
In 2022 the tightening monetary policy stance across advanced economies markedly increased risk-free rates at the global level and was associated with higher volatility in exchange rates and lower bond prices. The Federal Reserve System increased its policy rate by 4.5 percentage points, contributing to the marked appreciation of the US dollar of 8 percentage points in nominal effective terms. Higher policy rates transmitted to the longer end of the yield curve, leading to higher yields and lower prices of US bonds. For example, the yield on the US Treasury bond with a three-year maturity – the typical duration of bonds held as official reserves by central banks – increased by 2.6 percentage points, while the total return index for the corresponding maturity fell sharply for the first time in two decades (Chart A, panel a).[2] Monetary policy decisions in other advanced economies also helped increase bond yields elsewhere, with three-year yields increasing by more than 2 percentage points on average across G7 countries, with the exception of Japan, which kept its yield curve control policy unchanged over most of the review period.
Chart A
US interest rates rose sharply and the exchange rate of the US dollar appreciated in 2022, leading to significant valuation effects in the currency share of official foreign exchange reserves
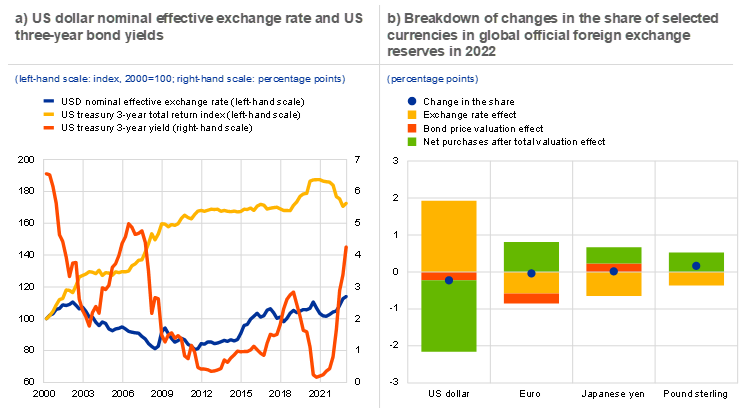
Sources: IMF, Federal Reserve Board and ECB calculations.
Notes: See footnote 31 for an explanation of the underlying calculations of the valuation effects and net purchases. The latest observation in panel a is for 31 December 2022.
Because of the significant swings in bond prices and exchange rates that took place in 2022, changes in currency shares of global foreign exchange reserves measured at current exchange rates are influenced by large valuation effects.[3] Chart A, panel b shows the breakdown of changes in the share of major reserve currencies by bond valuation effects, exchange rate valuation effects and net purchases in 2022.[4] The strengthening of the dollar exchange rate against other currencies contributed to an increase in the share of the US dollar of almost 2 percentage points. Other key reserve currencies experienced large negative exchange rate valuation effects as the US dollar strengthened across the board. By contrast, the share of the euro and the Japanese yen in global foreign exchange reserves declined by around half a percentage point owing to these exchange rate valuation effects. Moreover, bond price valuation effects were negative for the US dollar and the euro, as yields on bonds denominated in both currencies rose faster than on those denominated in other official reserve currencies.[5]
Official reserve managers tried to manage their portfolios actively to offset the effect of exchange rate movements in 2022. The green bars in Chart A, panel b suggest that the impact of the appreciation of the US dollar on foreign reserve shares was offset by net sales of US dollar assets and by net purchases of reserve assets denominated in currencies other than the US dollar. In fact, official reserve managers were net sellers of assets in US dollars in 2022 to the tune of around USD 293 billion, the largest net sales (in value terms) since 2000.[6] These sales would have translated into a decline of almost 2 percentage points in the share of the dollar in global official foreign exchange reserves in the absence of other effects. Foreign exchange interventions, where central banks use their foreign exchange reserves to influence the level or volatility of their exchange rate, accounted for a fraction of the net sales of US dollars in the review period. For instance, between September and October 2022, the Japanese authorities sold dollar reserves to purchase around JPY 9.2 trillion (more than USD 60 billion) in the foreign exchange market in a context of depreciation and volatility in the Japanese yen exchange rate against the US dollar, which they regarded as excessive. In the case of the euro, net purchases were positive, amounting to approximately €50 billion and contributing to a change in the share of the euro of almost 1 percentage point in 2022.
Developments in 2022 are illustrative of conventional reserve management strategies used by central banks. On a longer-term perspective, exchange rate fluctuations are the main drivers of valuation effects, while bond price changes play a much smaller role. Chart B, panel a shows the decomposition of changes in the share of euro-denominated reserves since 2000. Exchange rate effects, the yellow bars in the chart, account for most of the valuation effects and contributed to large increases in the share of the euro in 2002-03 and the significant decline in 2014-15. Valuation effects have been partially offset by net purchases of foreign currency reserves held in euro on 16 occasions over the past 23 years. However, the effects of exchange rate and bond price movements have rarely been fully offset. Developments for the US dollar are similar: exchange rate effects have been a major factor driving US dollar reserve shares and net purchases have partially offset these valuation effects.[7]
Patterns in active management of reserve currencies shown so far are generally in line with the available evidence for US dollar reserves. Chinn et al. (2022) show that central banks tend to reduce (increase) their holdings of US dollar assets following a dollar appreciation (depreciation), although this only partially offsets the impact of exchange rate movements on their portfolios.
IMF COFER quarterly data can be used to extend the analysis of Chinn et al. (2022) to other major reserve currencies since 1999. The analysis also includes the impact of exchange rate and bond valuation effects.[8] The average elasticity of reserve currency shares to these valuation effects can be estimated by regressing changes in reserve currency shares on changes in valuation effects. An estimated unity coefficient suggests that central banks let the currency composition of their reserve holdings move freely in response to valuation effects. A zero coefficient, instead, implies that central banks rebalance their portfolios fully to keep currency shares constant.
Chart B
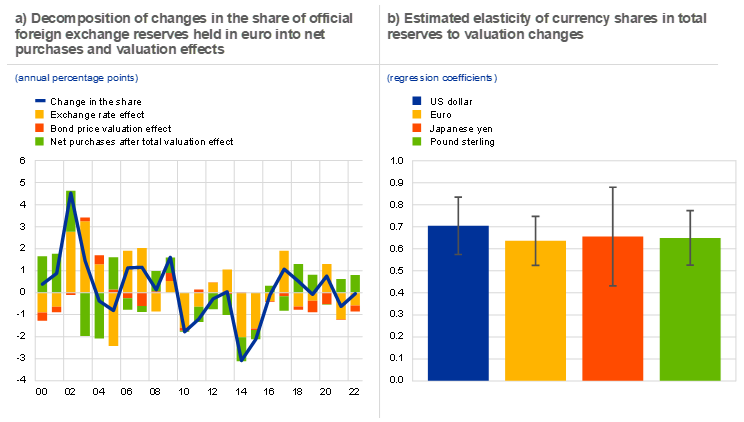
Source: IMF and ECB calculations.
Notes: See footnote 31 for an explanation of the underlying calculations of the valuation effects and net purchases. Elasticities are computed following Chinn et al. (2022) by estimating for each major reserve currency the regression: , where is a proxy for the change of the currency share owing to valuation effects. We use data from the first quarter of 1999 to the fourth quarter of 2022. The latest observation in both panels is for the fourth quarter of 2022.
Overall, the estimates suggest that patterns for the US dollar extend to other major reserve currencies, including the euro. Official reserve managers partially rebalance their reserves in US dollars as well as reserves in euro, pound sterling and Japanese yen. As shown in Chart B, panel b, all coefficients are statistically different from zero and from one, meaning that rebalancing further to changes in the value of reserve assets is only partial. We find no evidence that the elasticity significantly differs across major reserve currencies, as confidence intervals overlap across all currencies considered. The coefficients range between 0.6 and 0.7, implying that valuation effects largely explain quarterly changes in currency shares, while 30% to 40% of these are offset by active portfolio management.
All in all, valuation effects tend to exert a dominant influence on changes in the shares of major reserve currencies at short frequencies. The developments observed in 2022 were in line with historical regularities: the strong appreciation of the US dollar was offset by net sales of US dollar assets and net purchases of assets denominated in other major reserve currencies.



