- The Pound Sterling slumps on lower-than-anticipated UK CPI data for February.
- Soft UK inflation reinforces market expectations for the BoE to begin reducing interest rates in August.
- The Fed’s monetary policy meeting will guide the next move in the US Dollar.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) falls sharply in Wednesday’s London session as the United Kingdom Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported softer-than-expected Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for February. Annual headline and core inflation decelerated to 3.4% and 4.5%, respectively. Lower inflation is expected to allow Bank of England (BoE) policymakers to consider cutting interest rates earlier than what market participants had anticipated.
Investors should brace for high volatility in the Pound Sterling as the BoE is set to announce its second monetary policy decision of 2024 on Thursday. Investors are expecting the BoE to hold interest rates steady at 5.25%, but soft inflation data might allow policymakers to deliver slightly dovish guidance on interest rates.
Meanwhile, investors remain risk-averse ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) policy meeting, which will be announced at 18:00 GMT. Investors will keenly focus on the quarterly updated dot plot and economic projections as the Fed is expected to keep interest rates unchanged in the range of 5.25%-5.50%. The dot plot shows interest rate projections from Fed officials for various time frames.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling remains on backfoot ahead of Fed policy
- The Pound Sterling faces selling pressure as the United Kingdom ONS has reported softer-than-expected consumer price inflation data for February. The annual headline inflation significantly decelerated to 3.4% from expectations of 3.6% and the prior reading of 4.0%. The monthly headline CPI grew by 0.6%, rebounding from a similar decline seen in January. Investors anticipated the monthly headline inflation to grow at a higher pace of 0.7%.
- The annual core CPI, which strips off volatile food and energy prices, softened to 4.5% from estimates of 4.6% and the former reading of 5.1%. BoE policymakers generally consider the core inflation data as a preferred measure for decision-making on interest rates. Soft figures might increase their confidence that inflation will sustainably return to the desired rate of 2%. BoE policymakers have been reiterating that rate cuts would be appropriate only if they get convinced that the inflation target will be achieved.
- The Pound Sterling is expected to remain volatile as investors will shift focus to the Bank of England’s interest rate decision, which will be announced on Thursday. The BoE is expected to keep interest rates unchanged at 5.25% for the fifth time in a row. Investors will look for cues about when the BoE will start reducing interest rates. Currently, investors hope that the BoE will start reducing interest rates from the August meeting. The soft inflation data released on Wednesday is likely to reinforce these expectations.
- Meanwhile, the market sentiment remains cautious ahead of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decision. The CME FedWatch tool shows that the central bank is set to keep interest rates unchanged in the range of 5.25%-5.50%. With the no-change in interest rates almost fully priced in, the monetary policy statement, Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s press conference, and the dot plot, and economic projections will be in focus.
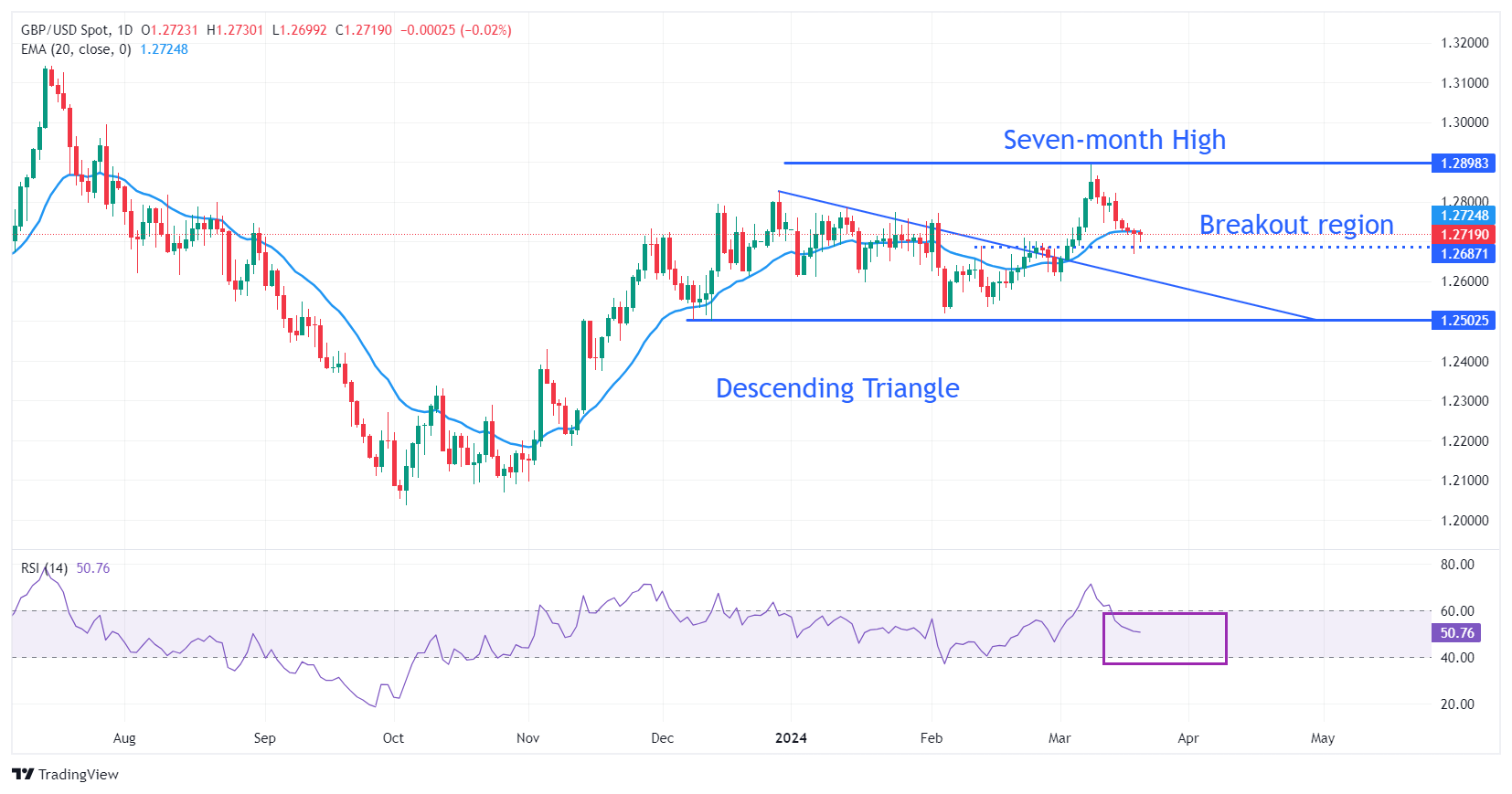
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling struggles to sustain above 1.2700
The Pound Sterling falls slightly below the breakout region of the Descending Triangle formed around 1.2700. The near-term demand for the GBP/USD pair remains uncertain as it struggles to sustain above the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.2730.
On the downside, the downward-sloping border of the Descending Triangle chart pattern will support the Pound Sterling. On the upside, a seven-month high at around 1.2900 will be a major barricade for the Cable.
The 14-period Relative Strength Index (RSI) returns to the 40.00-60.00 range, indicating a sharp volatility contraction.
Risk sentiment FAQs
In the world of financial jargon the two widely used terms “risk-on” and “risk off” refer to the level of risk that investors are willing to stomach during the period referenced. In a “risk-on” market, investors are optimistic about the future and more willing to buy risky assets. In a “risk-off” market investors start to ‘play it safe’ because they are worried about the future, and therefore buy less risky assets that are more certain of bringing a return, even if it is relatively modest.
Typically, during periods of “risk-on”, stock markets will rise, most commodities – except Gold – will also gain in value, since they benefit from a positive growth outlook. The currencies of nations that are heavy commodity exporters strengthen because of increased demand, and Cryptocurrencies rise. In a “risk-off” market, Bonds go up – especially major government Bonds – Gold shines, and safe-haven currencies such as the Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc and US Dollar all benefit.
The Australian Dollar (AUD), the Canadian Dollar (CAD), the New Zealand Dollar (NZD) and minor FX like the Ruble (RUB) and the South African Rand (ZAR), all tend to rise in markets that are “risk-on”. This is because the economies of these currencies are heavily reliant on commodity exports for growth, and commodities tend to rise in price during risk-on periods. This is because investors foresee greater demand for raw materials in the future due to heightened economic activity.
The major currencies that tend to rise during periods of “risk-off” are the US Dollar (USD), the Japanese Yen (JPY) and the Swiss Franc (CHF). The US Dollar, because it is the world’s reserve currency, and because in times of crisis investors buy US government debt, which is seen as safe because the largest economy in the world is unlikely to default. The Yen, from increased demand for Japanese government bonds, because a high proportion are held by domestic investors who are unlikely to dump them – even in a crisis. The Swiss Franc, because strict Swiss banking laws offer investors enhanced capital protection.