
Web3 signifies a fresh shift in how we interact online, aiming to give more control to individuals, nurture creative solutions, and shake up existing norms. But what makes it important? In this article, we’ll delve into its roots, unique attributes, and advantages, along with the hurdles and challenges it faces. Whether you’re simply intrigued by internet trends, want to start a digital venture, or are an experienced engineer, Web3 has a lot to offer you.
So, what’s Web3 and how did it originate?
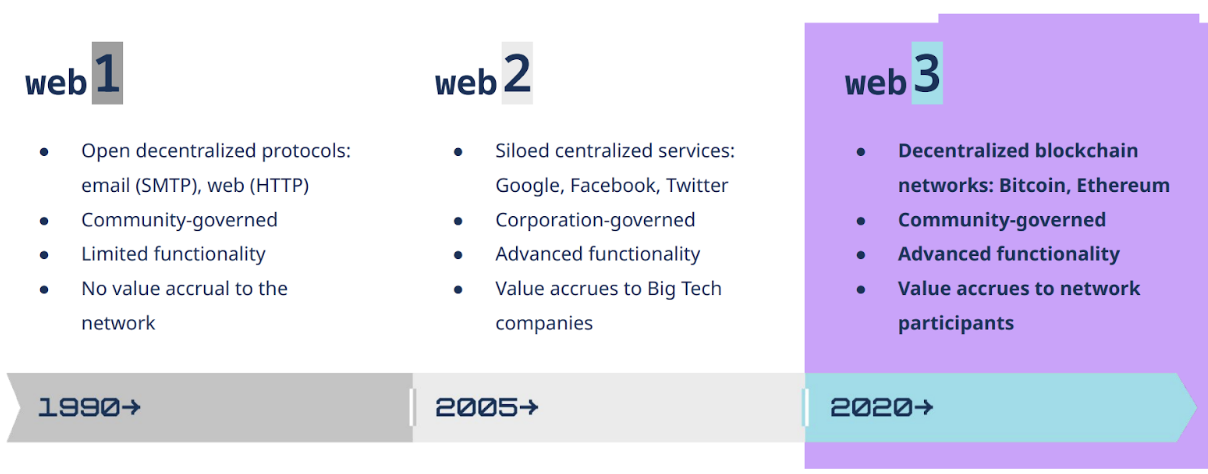
Web3 is seen as the next phase in the internet’s lifecycle, succeeding the earlier versions known as Web1 and Web2. These versions denote distinct epochs in the digital landscape, each adapting to what people need and expect from the internet.
Web1, active from the early 1990s until around 2004, is also called the “read-only” version of the web. Its primary function was to share fixed data—like scholarly papers, news stories, and personal blogs. Although this era enabled groundbreaking ways for people to communicate and collaborate globally, interactions were mostly unidirectional. Users could absorb data but had little to no room to alter or produce it as the content was static. Moreover, a handful of influential entities mostly centralized this digital space.
From 2004 to the present, the internet shifted to what’s known as Web2 or the “read-write” web. This change added elements of user involvement, dynamic content, and social connectivity. People could both consume and generate content, making the online world more inviting, varied, and engaging. However, this version brought reliance on intermediary services like search engines and social networks, which offer seemingly free or low-cost amenities but gather and monetise user information and attention in return. These middlemen subsequently gained significant sway over what appears online and how it’s managed.
Web3 is the unfolding chapter, sometimes referred to as the “read-write-own” web. This aims to bring back the internet’s original intent as a network that is not controlled by a single entity but is more community-driven, open, and interactive. Now, users can not only look at and generate content but also handle transactions and operate software without depending on external agents. The web becomes more secure, transparent, and fair. This is made possible by new technologies such as blockchain, smart contracts, peer-to-peer protocols, and cryptography. These technologies enable users to own their own data, control their own identity, and collaborate directly with others.
The 2008 release of the Bitcoin whitepaper marked a milestone in tech studies, tackling the longstanding challenge of getting many computers to agree on something without needing a centralized overseer. This obstacle, often referred to as the Byzantine fault, had been a roadblock to creating an internet that’s not controlled by any one entity but it’s for the people, by open-source developers and creators.
This fresh internet framework allows people to engage in a multitude of activities and services without having to depend on middlemen or governing bodies. For example, users can send and receive money through cryptocurrencies, access complex financial products through DeFi, create and trade digital assets through NFTs, prove their identity, and more.
Web3 will have a multi-dimensional impact on our lives, governed by the following manifestations of the blockchain technology:
Cryptocurrency serves as an online version of currency, except they are overseen and authenticated by a distributed computer grid rather than a centralized institution. Cryptocurrencies play a crucial role in creating reliable economies of scale by aligning the motivations of those in the network through strategic reasoning and fiscal principles. This kind of money can provide people with more autonomy, secrecy, and streamlined ways to manage their finances, as well as pave the way for novel methods of asset development and swapping. Here are some aspects and advantages of digital coins:
Easy transactions: Making transactions with cryptocurrency is generally straightforward, inexpensive, and can be somewhat private. Users don’t have to depend on external entities like banking systems or money-moving services to carry out their fund transfers.
Decentralized systems: Unlike traditional systems, cryptocurrency networks don’t have a central weak link that can be exploited. The setup is spread out over numerous points that approve and log each transaction, rendering them less susceptible to malicious interventions, content control, or unethical practices.
New possibilities: Cryptocurrency enables users to access new forms of value creation and exchange, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), or decentralized applications (DApps). These innovations can provide users with more choices, opportunities, and benefits in various domains, such as lending, borrowing, gaming, art, or social networking.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi for short, represents an initiative that uses decentralized digital frameworks and open-access coding to fabricate diverse financial goods and services. The main ambition of DeFi is to lay the groundwork for a financial environment that is more egalitarian, candid, and equitable, all without depending on middlemen or controlling bodies.
DeFi has several advantages over the traditional financial system, such as:
Cost: DeFi cuts down or even eradicates those surcharges and broker fees normally incurred via go-betweens like banking institutions or trading platforms. Individuals can hang onto more of their funds by directly dealing with each other through built-in systems of trust.
Speed: The decentralized system has the potential to speed up transactions. Thanks to blockchain-based smart contracts, transactions are streamlined, devoid of any red tape or waiting periods. You can tap into your funds or holdings whenever and wherever you desire.
Security: With DeFi, users get to amp up the safety and confidentiality of their personal info and holdings. This data is stored on an unalterable and transparent digital ledger. You manage your own access keys and digital wallets, without having to entrust a third party to look after your details.
Innovation: DeFi can act as a catalyst for fresh thinking and trials in the monetary field. It sets up a stage where anyone can formulate and make use of a multitude of financial offerings without any bureaucratic hurdles. This means people can avail themselves of groundbreaking ways to manage and trade assets, and also tailored solutions that fit their needs.
Smart contracts: DeFi incorporates smart contracts—automatically fulfilled agreements running on blockchain—to shape guidelines that emulate conventional monetary services, but in a manner that’s more transparent and open to interfacing with other platforms. These contracts let people utilize basic financial elements (known as financial primitives) like lending, borrowing, asset swapping, investment strategies, risk mitigation, etc. By mixing and matching these basic elements, folks can generate intricate and novel financial offerings.
In the following year, we can expect for the traditional financial system to integrate Bitcoin and Ethereum exchange traded funds (ETFs), in a push towards broader crypto adoption.
Web3 introduces an innovative model for controlling personal identifiers, granting users greater authority and safety over their private details. In this decentralized ID setup, people can fashion their own digital personas that are both provable and safeguard privacy.
A prime instance of this is Worldcoin, initiated by Sam Altman, the strategic mind behind OpenAI, a hub aimed at broader AI advancements. The objective of Worldcoin is to establish a universally acceptable and dependable method for anyone around the globe to demonstrate they’re a genuine human and not a computerized entity or AI script.
While the systems put in place by Worldcoin have their limitations, and have already started being exploited, builders are creating more innovative systems of Proof Of Humanity. An important candidate to be aware of is proof through social connections. The basic idea is that your behavior on-chain and the social connections that you have developed act as “vouchers” towards the likelihood of you not being a bot.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs have been making headlines with their astronomical prices and popularity. Cutting through the chatter, these are special digital tokens signifying exclusive rights over unique, often limited, assets—be they virtual or tangible. The scope of NFTs is broad, extending into areas like art, music, gaming, sports, social media and more.
A particularly inventive facet involves what’s called “utility NFTs.” These tokens offer specific perks or accesses for those possessing them. For instance:
- They can signify possession of real-world things or privileges—like event passes, reward points, or tangible merchandise. This opens up fresh monetization avenues and cash flow possibilities for content producers and commercial names while also boosting consumer devotion and interaction. According to a16z, so far, NFT creators have earned more than $1.9 billion in royalty revenues.
- As mentioned in the section above, they can serve to construct character verification or esteem gauging protocols, through what are known as “soul-bound NFTs.” These specific tokens are tied to an individual’s persona and are non-transferable. They may serve as a way to confirm someone’s identity, skills, or accolades across various online platforms.
- Utility NFTs can further empower people to engage in decision-making within community-led virtual organizations. Holding such a token might confer the ability to vote, claim membership privileges, or even exert influence in communal choices. These tokens also have the potential to stimulate cooperative efforts and contributions from community participants.
How AI is impacting Web3
Large language models like GPT-4 have the potential to make it easier for people to access and understand the often complex world of blockchain and decentralized web technologies. Despite its promise, Web3 can be intimidating for newcomers due to its steep learning curve and technical requirements. To make this easier, several tools are using language models to simplify data querying from various blockchain networks.
When it comes to software that incorporates artificial intelligence to help with Web3, there are generally two types: those aimed at the general public and those designed for developers. On the consumer side, there are services like RSS3 that help users receive tailored information streams directly from Web3 platforms. This might include updates from specific projects or even posts from influencers in the blockchain community.
For developers, there are platforms such as AirStack, which provides straightforward API interfaces for pulling data from Web3 networks. Another significant player in this space is Dune, an open-source tool focused on data analysis and visualization within the Web3 ecosystem. These resources not only make it easier to interact with Web3, but they also offer robust analytics capabilities, covering everything from basic descriptive statistics to more advanced predictive and prescriptive analyses. These can help anyone—whether they’re users or developers—gain deeper insights into various aspects of Web3, such as how people are using it, how well it’s performing, and what future trends might look like.
Some of the biggest challenges Web3 is facing:
Regulatory: Operating mostly in a not-so-well-defined legal landscape, Web3 confronts an assortment of rules across multiple localities when it comes to blockchain-focused endeavors, be it cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, or decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). This muddles the field for users, builders, and investors interested in diving into the Web3 space. Plus, certain state bodies may not be too keen on Web3, given its knack for shaking up conventional systems of governance and fiscal streams. The challenge for Web3 lies in striking a chord between novelty and legislative compliance, and in creating constructive dialogue with rule-makers.
Product-market fit: Web3 intends to offer novel or enhanced fixes for long-standing challenges across multiple sectors like finance, media, gaming, or social networking. Yet, a lot of Web3’s current offerings are in their infancy in terms of evolution or public acceptance. They haven’t quite verified their value proposition, usability, scalability, or sustainability. Added to this, they could face pushback from pre-existing digital giants that have carved out large followings and market strongholds. For Web3 to take off, it must center its efforts on cracking actual issues for everyday people, and must articulate its pros convincingly.
Decentralization: Web3 aspires to be fully decentralized, meaning that no single entity or group can control or influence its operation, governance, or outcomes. However, many aspects are still centralized or semi-centralized, such as the infrastructure, protocols, platforms, or tokens that underpin it. Notably, some pivotal elements within Web3 are heavily bankrolled by venture capitalists (VCs), whose goals may not fully align with those of the wider community. Moreover, walking the path of total decentralization isn’t without its compromises; it could mean forfeiting some speed, operational ease, or safety nets. Web3 has to double-check that its decentralization ideals aren’t just for show but have actual substance, and that all involved parties get a just and transparent stake in shaping its future.
The road forward
While Web3 continues to pique interest and see more users jump on board, it’s also catching the attentive gaze of governance bodies and policy enforcers. The European Union has recently rolled out legislative measures to regulate the crypto market and limit anonymous transfers. Known as MiCA, the EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation represents a first-of-its-kind legal scaffold aimed at digital assets, set to go live in 2024. While the regulation’s objective is to curb illegal activities like money laundering, tax evasion and fraud, some crypto enthusiasts who value privacy and decentralization have voiced concerns. What’s certain is that the buzz around Web3 is undeniable, as more users adopt cryptocurrencies, NFTs, DAOs and other innovations that challenge the traditional web and institutional model.
As per European Union explanations, MiCA aspires to safeguard European citizens putting their money into digital assets, all while nurturing tech advances and keeping the EU an attractive hub. But cautionary notes have been struck by some thought leaders, who say the legal provisions could also raise stumbling blocks or sow seeds of doubt for crypto startups and developers. Hence, keeping an eye on how MiCA molds the Web3 space in the years ahead is crucial.
In conclusion, the Web3 framework harbors game-changing potential across a multitude of sectors, granting users greater control over their personal information and holdings. Fresh minds are flocking to the Web3 space at an unprecedented rate. Scholarly probes into the subject are speeding up, visionary offerings are hitting the market steadily, and crucial tech underpinnings are getting fine-tuned. Whether you love it or you hate it, this fast-approaching “new internet” is likely to come with some big changes to how we interact online.










