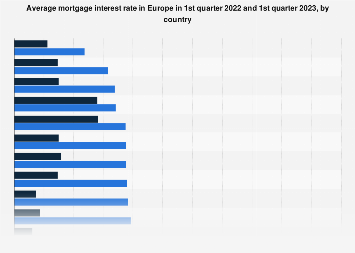
Mortgage interest rates soared in Europe in 2022, resulting in many countries seeing rates double in just a year. During the COVID-19 crisis, mortgage rates in Europe were at their lowest, as countries tackled the economic effects of the pandemic. With inflation rising, central banks gradually increased the interest rates, resulting in higher mortgage borrowing costs. In Hungary, the average mortgage interest rate reached close to 10 percent in the first quarter of 2023, up from about 3.5 percent in 2022.
Lower rates are for the financially savvy
Mortgage interest rates tend to be lower in the Nordic countries due to the financial stability and reliability of its borrowers. Other factors that influence the mortgage interest rates include inflation, economic growth, monetary policies, the bond market and the overall conditions of the housing market. More stable markets also tend to have higher average prices. France, Austria, the United Kingdom, and Germany have some of the highest new dwellings prices in Europe.
Larger economies show stability
The size of a country’s economy correlates to the stability of the interest paid on a mortgage. In countries such as Germany and France, interest rates remain under five percent, even after the interest hikes. Historically, these counties enjoyed interest rates below two percent.