On August 23, 2023, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
(SEC) announced1 the enactment of a series of new and
amended rules under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended
(the Advisers Act).2 We refer to these rules
collectively as the Private Funds
Rules.3 According to the SEC, consistent with
its mandate, the new rules are designed to address conflicts of
interest and adviser practices that may impose significant risks
and harms on investors and private funds. While the rules will have
a significant impact on the way advisers operate their businesses
and interface with investors, as adopted, the rules did not go as
far as many industry participants had feared based on the proposed
rules issued earlier in 2023.4
The Private Funds Rules include new and amended rules of
significant import to managers of private funds (Private Fund
Managers). Certain of the new rules apply only to Private Fund
Managers who are SEC-registered investment advisers (SEC-Private
Fund Managers). Others apply to Private Fund Managers generally,
irrespective of whether they are registered with the SEC or one or
more states, are exempt reporting advisers, or are prohibited from
registration. The Private Funds Rules also include changes
applicable to all SEC-registered investment advisers, including
advisers that are not Private Fund Managers. This Client Alert
summarizes the Private Funds Rules. In future alerts, we intend to
provide further in-depth guidance for Private Fund Managers
regarding changes to fund documents and the compliance policies and
procedures that will be necessitated by the new rules.
I. The Private Funds Rules
a. Scope
The SEC expressly applied certain of the Private Funds Rules (which
are described further below) to certain types of Private Fund
Managers. In short, SEC-Private Fund Managers must comply with the
Quarterly Statement Rule, the Audit Rule, and the Adviser-Led
Secondaries Rule (each as defined and discussed below). Private
Fund Managers5 must comply only with the Restricted
Activities Rule and the Preferential Treatment Rule (each as
defined and discussed below).
The SEC also enacted an amendment to Section 206(4)-7 of the
Advisers Act (the Compliance Rule), which is applicable only to
SEC-registered investment advisers (RIAs), including RIAs that are
not Private Fund Managers.
b. The Quarterly Statement Rule
In a new rule intended to enhance transparency to investors, Rule
211(h)(1)-2 (the Quarterly Statement Rule) requires SEC-Private
Fund Managers (and Private Fund Managers required to be registered
with the SEC)6 to distribute a quarterly statement to
the underlying investors in each private fund they manage that
includes specified information regarding fees, expenses, and
performance.7 The release also sets forth certain
delivery and formatting requirements with respect to such quarterly
statement(s) as follows:
- If the private fund is not a fund of funds, the statement must
be distributed within 45 days after the end of each of the first
three fiscal quarters of each fiscal year and 90 days after the end
of each fiscal year. - If the private fund is a fund of funds, then the statement must
be distributed within 75 days after the end of each of the first
three fiscal quarters of each fiscal year and 120 days after the
end of each fiscal year.
The Quarterly Statement Rule requires consolidated reporting for
substantially similar pools of assets to the extent doing so would
provide more meaningful information to investors and would not be
misleading.
The SEC also amended Section 204-2 of the Advisers Act (the
Recordkeeping Rule) so that SEC-Private Fund Managers will be
required to retain (a) the statements sent; (b) a record of each
addressee and the date(s) sent; (c) all records evidencing
calculations for expenses, rebates, etc.; and (d) records
substantiating the SEC-Private Fund Manager’s determination
that a private fund client is a liquid fund or an illiquid fund (as
that determination dictates some of the information to be included
on such statements).
c. The Mandatory Audit Rule
Rule 206(4)-10 (the Audit Rule) requires SEC-Private Fund Managers
(and Private Fund Managers required to be registered with the SEC)
to obtain an annual financial statement audit of the private funds
they advise. The financial statement audit must comply with Rule
206(4)-2 of the Advisers Act (the Custody Rule). This
“new” requirement will not be seen as a departure from
current practice for most SEC-Private Fund Managers who already
have their funds audited in order to comply with the Custody Rule,
as such audits would (and do) satisfy the Audit
Rule.8
d. The Adviser-Led Secondaries Rule
To address another discrete conflict identified by the SEC, Rule
211(h)(2)-2 (the Adviser-Led Secondaries Rule) requires SEC-Private
Fund Managers (a) to obtain a fairness opinion or valuation opinion
in connection with an adviser-led secondary transaction9
and to distribute such opinion to private investors prior to the
due date to elect to participate in such transaction, and (b) to
prepare and distribute to investors a summary of any material
business relationships between the SEC-Private Fund Manager or its
related persons and the independent opinion provider.
e. The Restricted Activities Rule
Rule 211(h)(2)-1 (the Restricted Activities Rule) restricts Private
Fund Managers from engaging in certain activities that the SEC has
determined to be contrary to the public interest and the protection
of investors unless such Private Fund Manager either (a) discloses
such activity or (b) discloses and receives consent for such
activity. To that end, the SEC explicitly lists which restricted
activities require disclosure and which restricted activities
require both disclosure and consent. The enumerated restricted
activities are as follows:
- Disclosure and Consent
- Charging or allocating to the private fund fees or expenses
associated with an investigation of the Private Fund Manager or its
related persons by any governmental or regulatory
authority10 - Borrowing money, securities, or other private fund assets, or
receiving a loan or extension of credit, from a private fund
- Charging or allocating to the private fund fees or expenses
- Disclosure Only
- Charging the private fund for any regulatory, examination, or
compliance fees or expenses of the Private Fund Manager or its
related persons - Reducing the amount of any adviser clawback by actual,
potential, or hypothetical taxes applicable to the Private Fund
Manager, its related persons, or their respective owners or
interest holders - Charging or allocating fees and expenses related to a portfolio
investment on a non-pro rata basis when more than one private fund
or other client advised by the adviser or its related persons has
invested in the same portfolio company
- Charging the private fund for any regulatory, examination, or
f. The Preferential Treatment Rule
Rule 211(h)(2)-3(a)(1) and (2) (the Preferential Treatment Rule)
prohibits Private Fund Managers from providing preferential terms
to certain investors in a private fund or a similar pool of
assets11 unless disclosed to current and prospective
investors. According to the SEC, this rule is designed to address
the material, negative effects of specific types of preferential
treatment on investors–typically effected through the
widespread use of side letters.12
Under the Preferential Treatment Rule, Private Fund Managers are
specifically prohibited from the following:
- Providing preferential terms to an investor (or investors)
relating to redemptions in a private fund or a substantially
similar pool of assets that the manager reasonably expects to have
a material, negative effect on other investors in the private fund
or substantially similar pool of assets - Providing preferential information regarding the portfolio
holdings or exposures of a private fund, or of a substantially
similar pool of assets, if the manager reasonably expects that
providing such information would have a material, negative effect
on the other private fund investors
Beyond these specific prohibitions, Private Fund Managers are
generally prohibited from providing other types of preferential
treatment to select investors unless the manager provides written
notice of (a) preferential material, economic terms prior to an
investor’s investment in the private fund; (b) any other
preferential terms to all investors after the investor’s
investment; and (c) at least annually, any preferential terms made
available to investor(s) since the last notice.
In a departure from the proposed rule, with respect to
preferential redemption terms, the SEC will permit disparate
treatment (a) with respect to redemptions required by applicable
law, rule, regulation, or order of certain governmental authorities
and (b) if the manager has offered the same (preferential)
redemption right to all existing investors and will continue to
offer the same rights to all future investors in the private fund
or similar pool of assets.
With respect to access to preferential portfolio information for
select investors sometimes effected through side letters, also in a
change from the proposed rule, the Preferential Treatment Rule
permits such a practice only if the adviser offers such information
to all investors.
g. Related Recordkeeping Rule Changes
The Private Funds Rules also include an amendment to the existing
Recordkeeping Rule that requires SEC-Private Fund Managers to
retain certain records related to their compliance with the Private
Funds Rules.
II. Compliance Rule Annual Review Amendment
As part of the adoption of the sweeping new rules, the SEC
enacted an amendment to the Compliance Rule that requires
SEC-registered investment advisers, both SEC-Private Fund Managers
and RIAs, to document their annual review of compliance policies
and procedures in writing. Note, however, that the SEC explicitly
noted that the Compliance Rule changes do not mandate a specific
format of written documentation, leaving that to the discretion of
the adviser in order to “determine what would be
appropriate.” While, prior to this amendment to the Compliance
Rule, SEC-registered investment advisers were (and are) required to
conduct an annual review, the review was not required to be
documented in writing (although in practice many such advisers
document such reviews in writing).
III. Transition Period, Compliance Date, Legacy Status
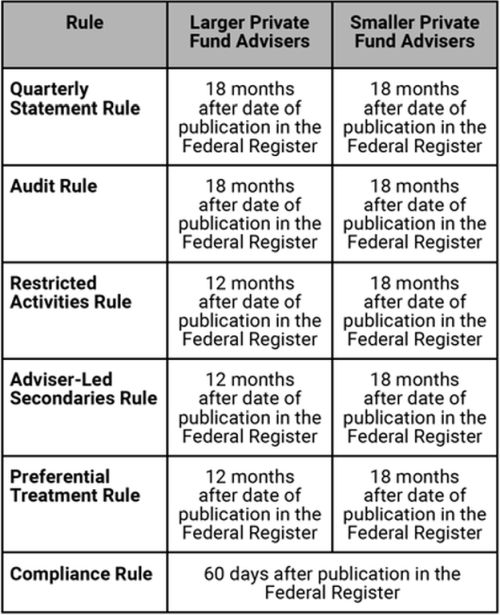
a. Transition Period; Compliance Date
The SEC set forth a timeline as to when a Private Fund Manager must
come into compliance with each applicable Private Funds Rule, which
varies based on the specific Private Funds Rule and whether the
Private Fund Manager is a “Larger Private Fund
Adviser”13 or a “Smaller Private Fund
Adviser,”14 which we have set forth immediately
below. However, it should be noted, as discussed further below,
that the SEC explicitly states which rules (or parts of rules)
require compliance on both a retroactive/backward-looking basis
(e.g., renegotiating contracts and revising existing fund
documents) and a go-forward basis.
b. Legacy Status
The SEC has provided for legacy status for the prohibitions
associated with the Preferential Treatment Rule and certain aspects
of the Restricted Activities Rule (i.e., the items that require
investor consent). The legacy status provisions apply to governing
agreements that were entered into prior to the compliance date if
the applicable rule would require the parties to amend the
agreements. Notwithstanding the 12-to-18-month lead time associated
with the effectiveness of the rules, we encourage Private Fund
Managers to audit their various fund documents and side letters as
soon as possible in order to determine which documents will need to
be renegotiated and/or amended and which will be
“grandfathered” as a result of the legacy status
described above.
IV. Conclusion
As we will explore in greater detail in subsequent alerts,
because of a lack of clarity on some items and a wide berth of
discretion offered to advisers on others, the Private Funds Rules
are likely to give rise to a wide dispersion in compliance and
other market practices among Private Fund Managers in the months to
come. For instance, for practices that are not prohibited by the
rules but are clearly frowned upon by the SEC, the new enhanced
disclosure requirements may cause some long-standing practices to
fall by the wayside. And while the Private Funds Rules do not go as
far as many industry participants had feared based on the proposed
rules, the adopting release suggests continued scrutiny of Private
Fund Managers in a number of areas in which there is no new
rulemaking. For instance, the discussion of the fiduciary duties of
Private Fund Managers contained in the rule adopting release cites
specific concerns related to the rights of Private Fund Managers to
be indemnified by their private fund clients except in the case of
(what the SEC clearly views to be an elevated standard of) gross
negligence and on their receipt of fees for unperformed services.
Even though the SEC chose not to proceed with rulemaking to address
these concerns, we expect these areas to continue to invite
scrutiny in SEC examinations and investigations. Lastly, while the
SEC regulates, among others, Private Fund Managers, the Private
Funds Rules seem to imply that they now regulate their advised
funds as well, narrowing the distinction between private funds and
registered funds. We will continue to monitor any releases and/or
guidance from the SEC on any of the topics described herein.
V. Next Steps
The adoption of the Private Funds Rules and the associated
amendments to the Compliance Rule and the Recordkeeping Rule will
necessitate changes to the fund documents and compliance programs
of all Private Fund Managers. From time to time, in advance of the
effective date, Lowenstein Sandler will be releasing additional
Client Alerts that explore, in greater detail, these important
developments to enable clients to update their governing documents
and compliance policies and procedures in order to navigate the
increasingly treacherous regulatory landscape. We will also monitor
not only these regulatory changes but the market practices that
evolve to address them.
Footnotes
1. https://www.sec.gov/news/press-release/2023-155.
The SEC Chair and several Commissioners also released public
statements on its release. See https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/gensler-statement-private-fund-advisers-082323,
https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/crenshaw-statement-private-fund-advisers-082323,
https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/uyeda-statement-private-fund-advisers-082323,
https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/lizarraga-statement-private-fund-advisers-082323
and https://www.sec.gov/news/statement/peirce-statement-doc-registered-investment-adviser-compliance-reviews-08232023.
2. The final Private Funds Rule will become effective 60
days after publication in the Federal Register.
3.
https://www.sec.gov/files/rules/final/2023/ia-6383.pdf. See
also https://www.sec.gov/files/ia-6383-fact-sheet.pdf.
5. It should be noted that “[t]he final quarterly
statement, audit, adviser-led secondaries, restricted activities,
and preferential treatment rules do not apply to investment
advisers with respect to securitized asset funds they advise. All
references to private funds shall not include securitized asset
funds.”
6. SEC-Private Fund Managers are not required to do this
if such statements that comply with the Quarterly Statement Rule
are distributed by another person.
7. We will expand on the requirements of the Quarterly
Statement Rule, including the specific information to be included
in quarterly statements, in a subsequent Client Alert.
8. Because surprise examinations do not meet the
requirements of the Audit Rule, they are effectively eliminated as
an option for private funds advised by SEC-Private Fund
Managers.
9. A “secondary transaction” occurs when an
investment manager initiates a transaction offering its private
fund investors the option of either selling all or a portion of
their interests in a private fund advised by such manager or
converting or exchanging such interests for new interests in a new
fund advised by such manager.
10. Regardless of any disclosure or consent, under the
rule, an adviser may not charge or allocate fees and expenses
related to an investigation that results in or has resulted in the
imposition of a sanction by a court or governmental authority for a
violation of the Advisers Act or the rules promulgated
thereunder.
11. The SEC has not defined “similar pool of
assets,” however, the term’s inclusion is designed to
capture most commonly used private fund structures in order to
prevent advisers from structuring around prohibitions on
preferential treatment.
12. While the new rules do not expressly dictate the
prohibition of or reduction in the use of side letters (as was
originally feared by some), we expect that the enhanced disclosure
requirements described in this section may have a chilling effect
and present practical challenges with respect to previously
negotiated commercial terms, and accommodations going forward for
investors who have historically become accustomed to preferential
terms.
13. Private Fund Managers with $1.5 billion or more in
private funds assets under management.
14. Private Fund Managers with less than $1.5 billion in
private funds assets under management.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general
guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought
about your specific circumstances.